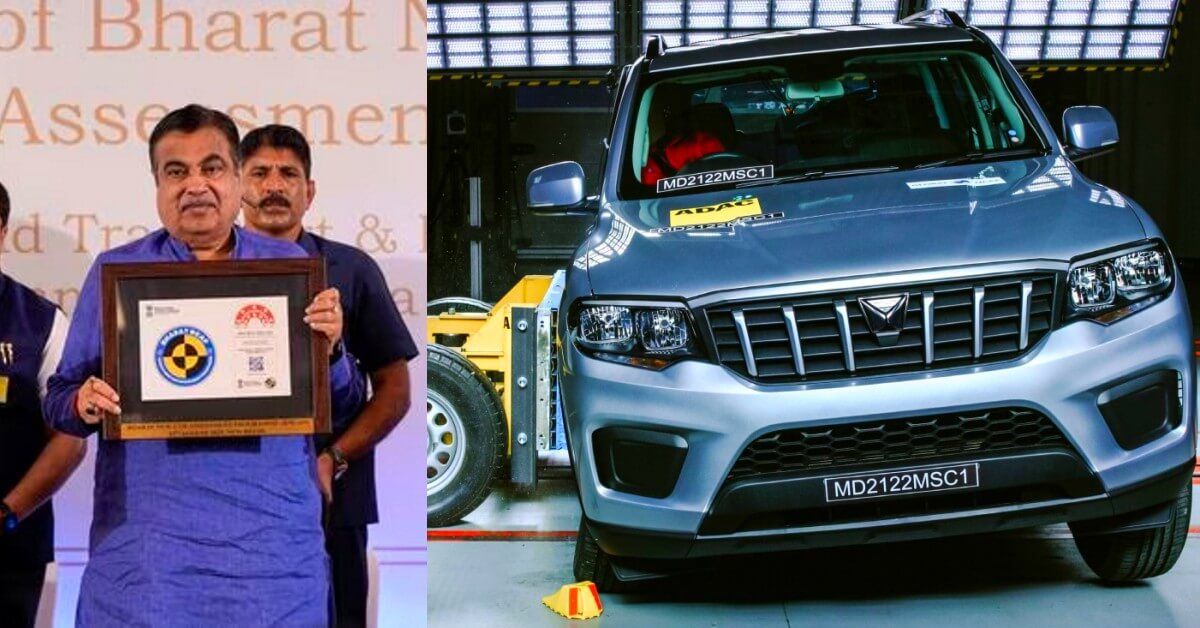
Bharat NCAP crash test outcomes: Top cars to get 5-star ratings
Published On 25/5/2024, 5:14:29 am Author Nitesh YadavIndia’s roads are teeming with activity, but unfortunately, they also witness a significant number of accidents. Acknowledging the urgent need for safety, the Indian government launched the Bharat NCAP (New Car Assessment Program) in 2018. Let’s explore the motivations for its establishment and how it stacks up against the internationally acknowledged Global NCAP and which Indian cars got 5 star ratings.

In the past, popular cars like the Scorpio and Swift received poor safety ratings from the Global New Car Assessment Program (NCAP), causing concern among Indian buyers. The Global NCAP, while designed for international standards, overlooked the unique conditions of Indian roads, leaving a significant blind spot in its assessment.
However, the tide began to turn when the Tata Nexon won a 5-star safety rating from the Global NCAP. This achievement sparked a revolution in the Indian automotive industry, leading to a rise in safety-conscious consumers. It was a clear signal that Indian consumers were ready to prioritize safety over other factors such as after-sales service.
Recognizing this shift in consumer behavior, the Indian government introduced the Bharat NCAP in 2018. Unlike its global counterpart, the Bharat NCAP was specifically designed to address the unique road safety needs of India. It aimed to empower Indian car buyers to make informed choices, putting the safety of lives above all else.
Key considerations in Bharat NCAP
The Bharat New Car Assessment Program (Bharat NCAP) is a safety assessment program specifically designed for India. Here are the key considerations:
Scope: The program applies to passenger vehicles with a Gross Vehicle Weight (GVW) of up to 3500 kg.
Assessment Areas: Vehicles are evaluated in three main areas:
Adult Occupant Protection (AOP) Child Occupant Protection (COP) Safety Assist Technologies (SAT)
Test Protocols: Each car undergoes several tests, including frontal impact, side impact, side pole impact, electronic stability control, and pedestrian-compliant front design. The performance of airbags and seatbelts, two critical safety components of a car, are also assessed.
Publication of Results: The results of the assessments are published, providing consumers with an indication of the level of protection offered to the occupants.
Validity and Applicability of Star Rating: The star rating given to a vehicle model is based on its performance when evaluated under the three areas of assessment.
Recent cars with 5 stars in Bharat Ncap
VW Virtus

Skoda Slavia

Hyundai Verna