How to Use Your Car's OBD Port: A Comprehensive Guide
Published On 19/7/2024, 7:25:42 pm Author Uttkarsh SinghDiscover the importance of your car's OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) port in this comprehensive guide. Learn how the OBD port functions as a gateway to your vehicle's diagnostic system, enabling you to monitor performance, identify issues, and perform routine checks with ease.

An OBD scanner is like a blood test for your car. It provides many diagnostic reports. This tool shows you the health and performance of your vehicle. By connecting to the OBD port, you can monitor engine performance, check for fault codes, and ensure everything runs smoothly. Whether you're a mechanic or a car owner, understanding the OBD scanner can save time and money.
How to use OBD Scanner
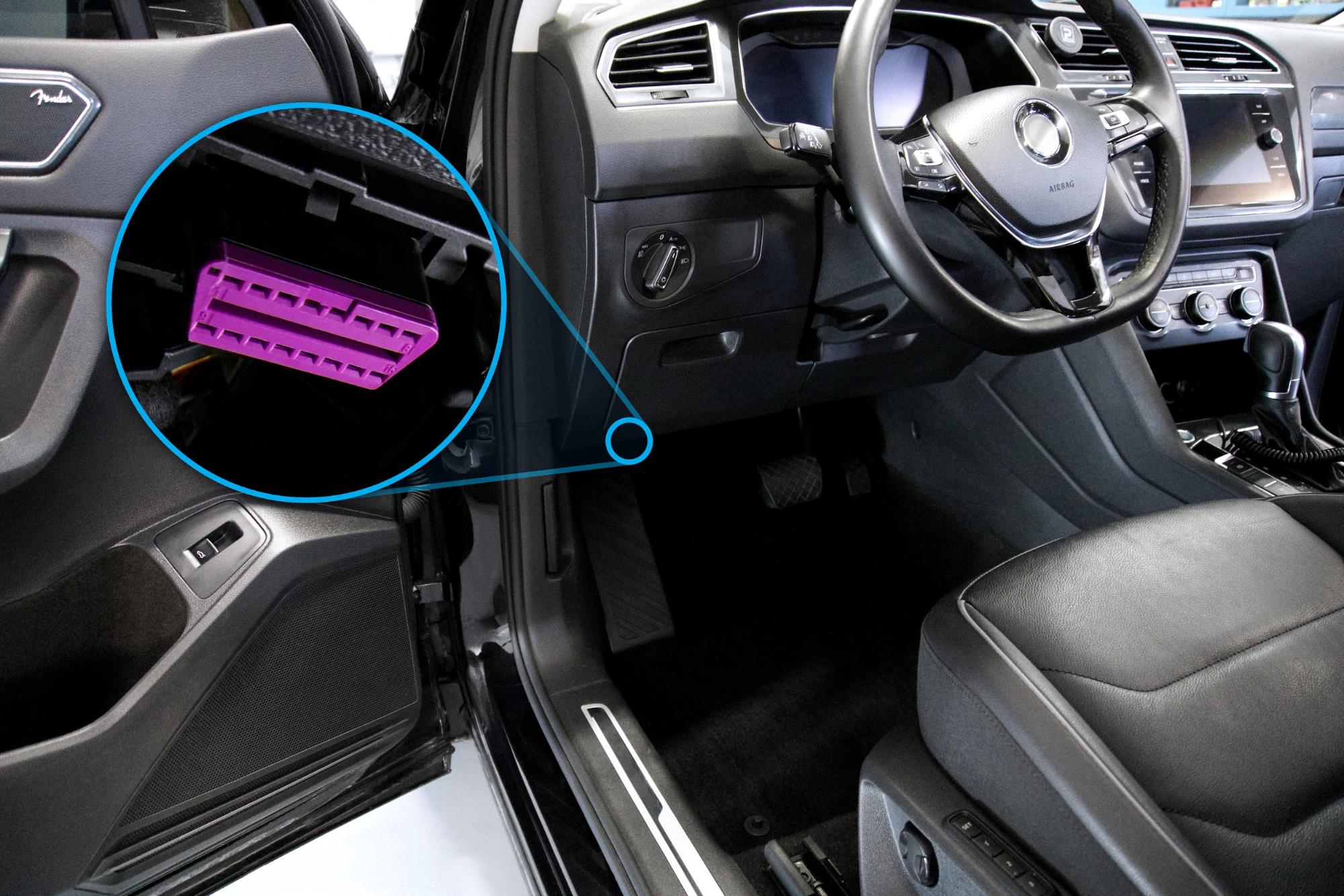
First things first, if you don't have an OBD scanner, you'll need to get one. Think of it as a stethoscope for your car. Now, let's find the OBD port. It's usually located under the dashboard on the driver's side. You might have to do a bit of contorting to see it.
Once you locate the port, take your OBD scanner and insert the connector into the port. It should fit snugly, like plugging in your phone charger. The scanner will light up, signaling it's ready to communicate with your car. And there you go!
How does OBD Scanner gather data
An OBD (On-Board Diagnostics) scanner retrieves data from a vehicle's onboard computer systems, which monitor and manage various functions of the car. Modern vehicles are equipped with numerous sensors and electronic control modules (ECMs) that continuously collect and process data. This data is stored within the ECMs, covering aspects like engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
To access this data, the OBD scanner connects to the vehicle through the OBD-II port, usually located under the dashboard near the driver's seat. This port provides a standardized interface for communication with diagnostic tools. The OBD system uses specific communication protocols, such as ISO 9141 or CAN, to format and transmit data from the ECMs through the port.
Once the OBD scanner is plugged into the OBD-II port, it establishes a connection with the vehicle’s data network. The scanner sends requests to the ECMs for specific data, such as diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) or real-time sensor readings. The ECMs then respond by transmitting the requested data back through the OBD-II port.
The scanner processes and decodes this data, displaying it on its screen. This information can include trouble codes that indicate specific issues, as well as live data from various sensors that provide real-time performance metrics. By interpreting this data, the OBD scanner helps technicians and vehicle owners diagnose problems and monitor the vehicle’s overall performance.
OBD scanners designed to work with mobile phones, allowing users to retrieve and view vehicle data on their smartphones or tablets. To interact with the OBD scanner, you need to download a compatible mobile app. Many OBD scanners come with their own apps, but there are also third-party apps available that can work with various OBD scanners. These apps are available for both Android and iOS devices.
Many mobile apps offer additional features, such as logging and exporting data, generating reports, and providing in-depth analysis. Some apps also integrate with other vehicle diagnostics and maintenance tools.
How OBD Scanner diagnose differently than Mechanics
Scope and Depth
OBD Scanner: Provides a basic overview of vehicle health and can read and clear trouble codes. It is useful for quick diagnostics and routine checks but might lack depth in detailed analysis.
Mechanics: Professional mechanics use advanced diagnostic tools and techniques to perform a more thorough and comprehensive analysis. They can interpret data from multiple sources, conduct physical inspections, and perform tests beyond what an OBD scanner can provide
Complex Diagnostics
OBD Scanner: Primarily focuses on electronic and sensor-related issues. It might not be able to diagnose mechanical problems or issues that don’t trigger trouble codes. Mechanics: Have the expertise and tools to diagnose complex mechanical issues, perform detailed inspections, and carry out repairs. They use a combination of diagnostic tools, manual testing, and experience to identify problems that may not be detected by an OBD scanner alone.
Specialized Tools
OBD Scanner: Offers standardized diagnostics based on OBD-II protocols. While it can provide useful information, it might not support manufacturer-specific tests or advanced functionalities.
Mechanics: Utilize specialized tools and equipment for manufacturer-specific diagnostics, performance testing, and repair. These tools can access deeper vehicle systems and provide more detailed insights.
Expert Interpretation
OBD Scanner: Provides raw data and codes that require interpretation. Users need some level of understanding to diagnose issues based on the information provided. Mechanics: Have the expertise to interpret data from various diagnostic tools, combine it with physical inspections, and make informed decisions about repairs and maintenance.
Why you should get an OBD Scanner
A car has over 30,000 parts, and most people aren't aware of the complexity involved in keeping a vehicle running smoothly. Understanding the basics of vehicle diagnostics is crucial for anyone who owns a car. By familiarizing yourself with how these systems work and investing in an OBD scanner, you can gain valuable insights into your vehicle's health.
An OBD scanner is a practical tool for car owners because it provides a direct line to your vehicle's computer systems. It helps you monitor and diagnose issues by reading trouble codes, tracking real-time data, and offering insights into various performance metrics. This allows you to detect potential problems before they escalate, potentially saving you from costly repairs and breakdowns.
Moreover, knowing the basics of vehicle diagnostics empowers you to keep a mechanic in check. When you're informed about how your vehicle's systems function and what the OBD scanner reveals, you can better understand the recommendations and diagnoses provided by professional mechanics. This knowledge helps you make informed decisions about repairs and maintenance, ensuring that you’re not oversold on unnecessary services.
If you liked this article, you might like this one too! [https://carwyapar.com/news/india-car-news/dilip-chhabria-modified-cars-from-90s-till-today-009399]